Teachers play a crucial role in fostering emergent writing skills through various strategies and activities. Here's how teachers typically facilitate this process:
1. Creating a Print-Rich Environment:
- Classroom Materials: Teachers ensure that classrooms are filled with writing materials such as markers, crayons, pencils, paper, whiteboards, and other tools that encourage writing.
- Writing Centers: Establish dedicated writing centers where children can freely access writing materials and engage in writing activities independently or collaboratively.
2. Modeling Writing Behaviors:
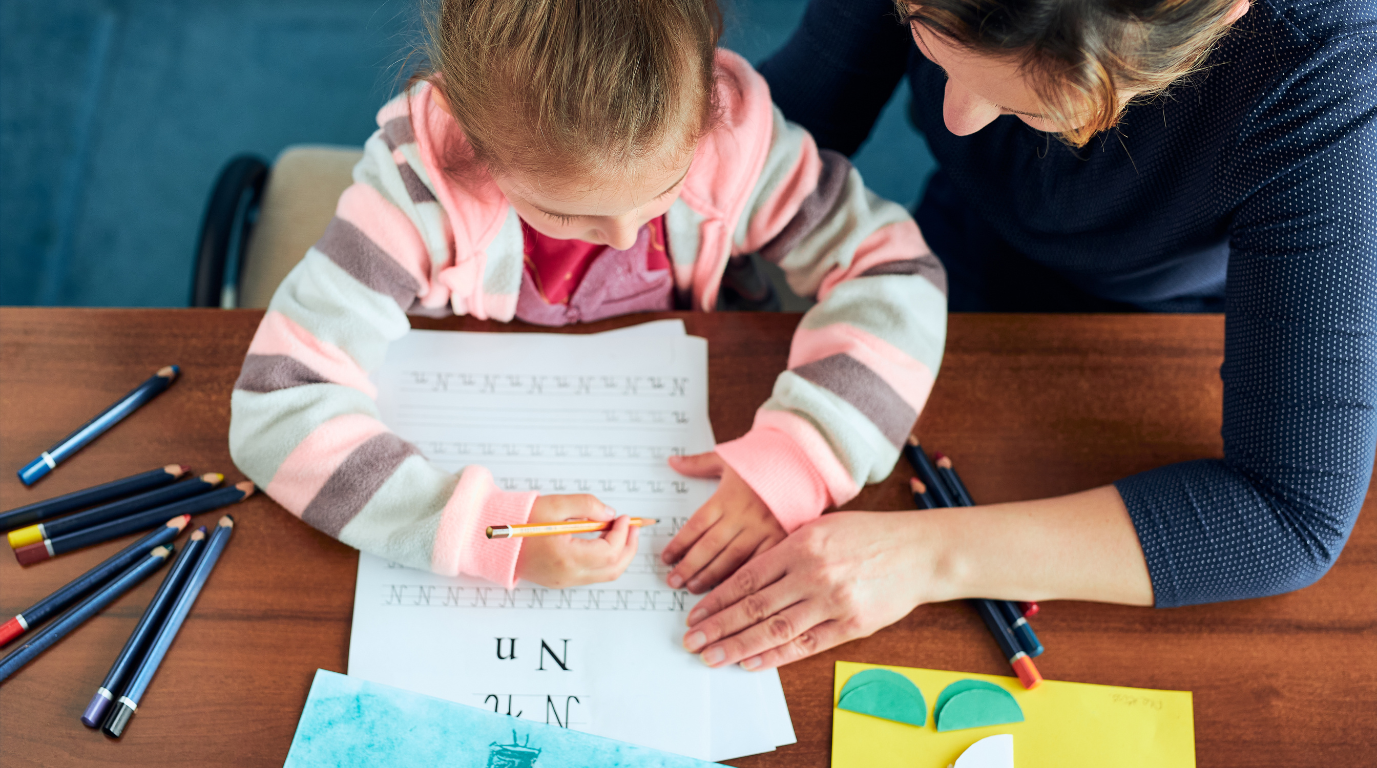
- Demonstration: Teachers model writing behaviors by writing in front of the class. They might narrate their writing process, discussing their thoughts aloud while demonstrating how to form letters, words, or sentences.
- Shared Writing: Engage children in shared writing experiences where the teacher and students collaborate to write stories, class messages, or charts together.
3. Encouraging Writing Activities:
- Drawing and Dictation: Teachers encourage children to draw pictures and then dictate or tell stories related to their drawings. This allows children to express themselves verbally while associating their spoken words with written text.
- Writing Journals: Provide children with writing journals or notebooks where they can freely practice writing, scribbling, or forming letters and words.
4. Supporting Fine Motor Skills:
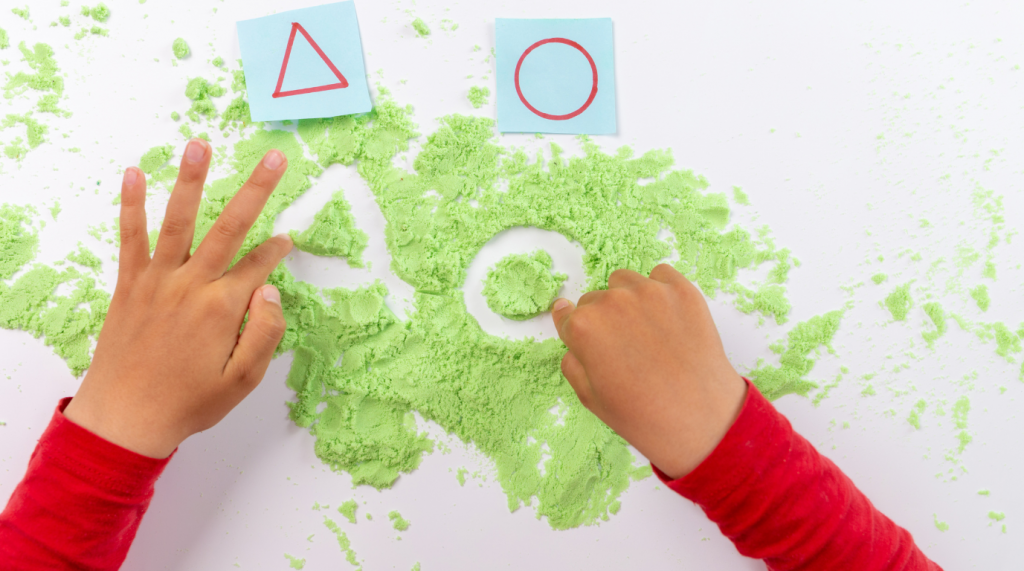
- Fine Motor Activities: Incorporate activities that strengthen fine motor skills, such as finger painting, using playdough, threading beads, or tracing lines and shapes. Improved fine motor skills contribute to better writing control.
- Proper Grip: Teachers provide guidance on holding writing tools correctly, supporting children in developing a comfortable and effective pencil grip.
5. Encouraging Literacy Experiences:
- Reading Connections: Connect emergent writing with reading experiences. Encourage children to “read” their own writing or shared class writing. This helps them understand that written text carries meaning.
6. Positive Reinforcement and Feedback:
- Encouragement: Provide positive reinforcement and encouragement for children’s writing attempts. Acknowledge and celebrate their efforts, valuing their progress and creativity.
- Constructive Feedback: Offer gentle guidance and feedback that supports improvement without discouraging children’s attempts at writing.
7. Individualized Support:
Differentiated Instruction: Recognize and support each child’s unique progress in writing. Provide individualized support based on each child’s developmental stage, offering tailored guidance and activities.
Teachers employ these strategies to create a supportive and stimulating environment that encourages children to explore writing, experiment with letters and forms, and gradually develop emergent writing skills at their own pace. Through these activities, teachers help lay the groundwork for future writing proficiency.

10 Way Parents Can Help their Child with Oral Communication:
Parents can play a significant role in nurturing their child’s emergent writing skills at home. Here are several ways parents can support and encourage their child’s development in emergent writing:
- Provide Writing Materials: Offer a variety of writing materials such as crayons, markers, pencils, colored pencils, chalk, and different types of paper. Having access to these materials encourages children to explore and experiment with writing.
- Create a Writing Area: Designate a space at home as a writing area. Stock it with writing tools, blank paper, notebooks, and other materials to make writing easily accessible and inviting.
- Encourage Scribbling and Drawing: Encourage children to scribble, draw, and create pictures. Emphasize the enjoyment of the process rather than focusing solely on the end result. Scribbling is an early form of writing and helps children develop control over writing tools.
- Model Writing Behaviors: Demonstrate writing behaviors by writing in front of your child. Narrate your thoughts while writing, discussing what you are writing and why. This helps children understand the purpose of writing.
- Engage in Shared Writing Activities: Collaborate on writing tasks. Ask your child to dictate a story or a message while you write it down. This shows the connection between spoken language and written text.
- Practice Writing Their Name: Start with helping your child learn to write their name. Use a large font and guide them in tracing the letters. This helps children recognize and spell their own name, which is personally meaningful to them.
- Encourage Storytelling and Dictation: Prompt your child to tell stories or describe their drawings. Record their stories or dictate them as they tell you, helping them see the connection between spoken and written words.
- Celebrate and Display Their Writing: Display your child's writing and drawings on a bulletin board or the refrigerator. Celebrate their efforts and show appreciation for their creations.
- Provide Writing Prompts: Offer simple writing prompts or questions to inspire writing. For instance, ask about their favorite toy, what they did during the day, or what they want to do tomorrow.
- Praise Efforts and Encourage Creativity: Offer praise and encouragement for their attempts at writing. Focus on effort and progress rather than perfection. Encourage creativity and imagination in their writing endeavors.
By providing a supportive environment and engaging in various writing activities, parents can foster their child’s emergent writing skills. Encouraging exploration, creativity, and a positive attitude toward writing helps children develop confidence and interest in the writing process.